Respiratory System Cell Types
Respiratory system cell types. Allergies common cold coronavirus infections streptococcal infections whooping cough. Respiration is an everyday term that is often used to mean breathing Respiratory system function Respiratory systems allow animals to move oxygen needed for cellular respiration into body tissues and remove carbon dioxide waste product of cellular respiration from cells. There are two different types of lung cancer.
Seterra is a free online quiz game that will teach you about science biology chemistry and the anatomy of the human body. A breath is one complete respiratory cycle that consists of one inspiration and one expiration. Respiratory Volumes and Capacities.
The design of the respiratory system. The body cells need a continuous supply of oxygen for the metabolic processes that are necessary to maintain life. Human respiratory system the system in humans that takes up oxygen and expels carbon dioxide.
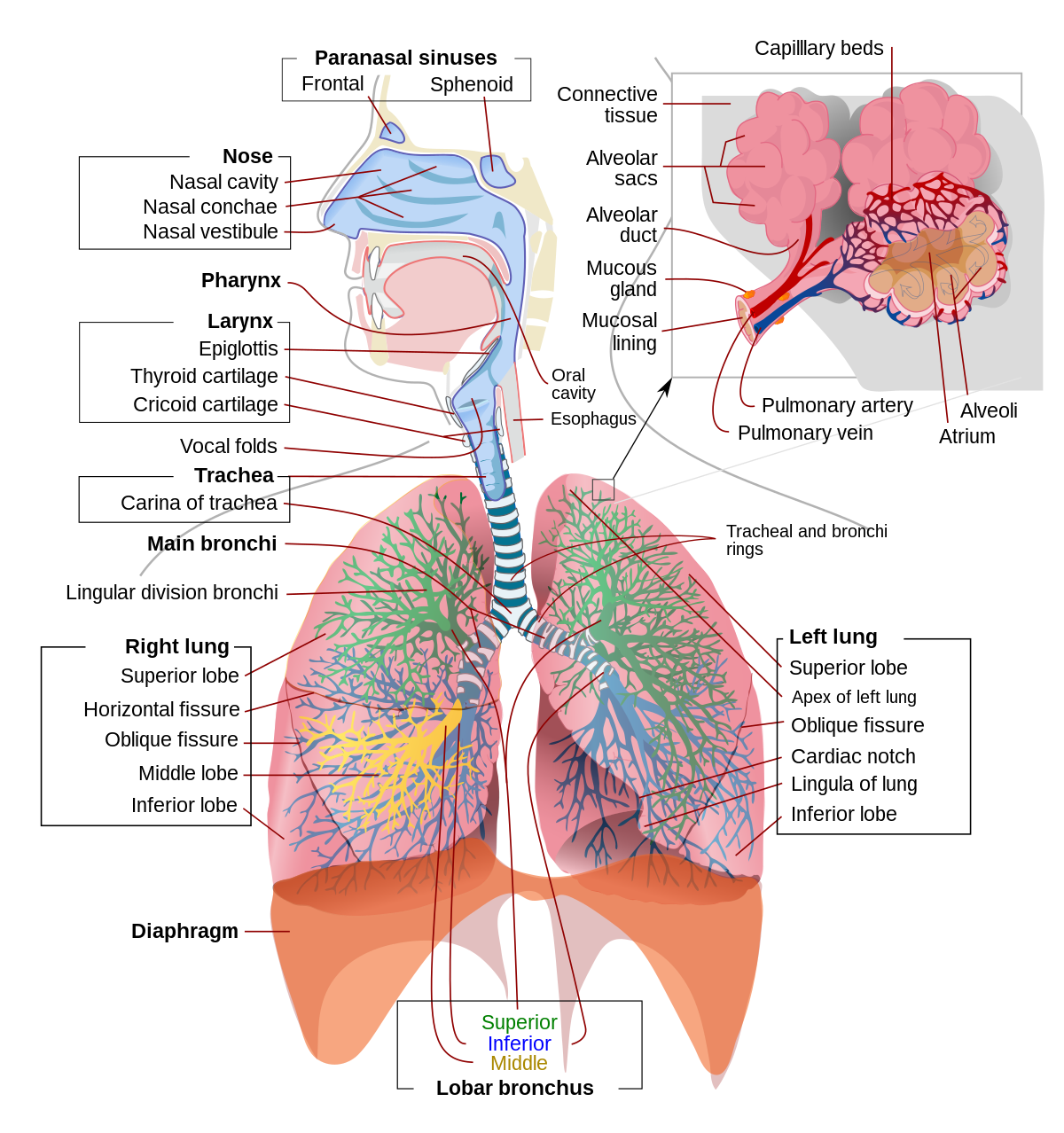
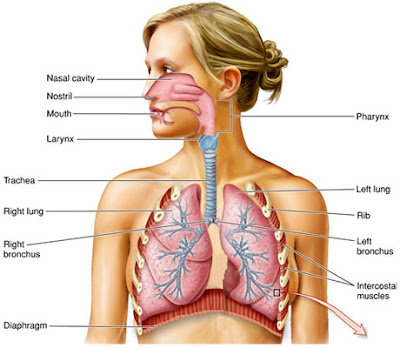
Contents Functions of the Respiratory System The flow of air from the nose to the lungs Roots suffixes and prefixes Cancer Focus Related Abbreviations and Acronyms Further Resources Functions of the Respiratory System The main role of the Respiratory System is the inhalation of fresh oxygen O2 needed by the bodys cells and the exhalation of waste carbon dioxide CO2. Under normal conditions the average adult takes 12 to 15 breaths a minute. The respiratory system is composed of a group of muscles blood vessels and organs that enable us to breathe.
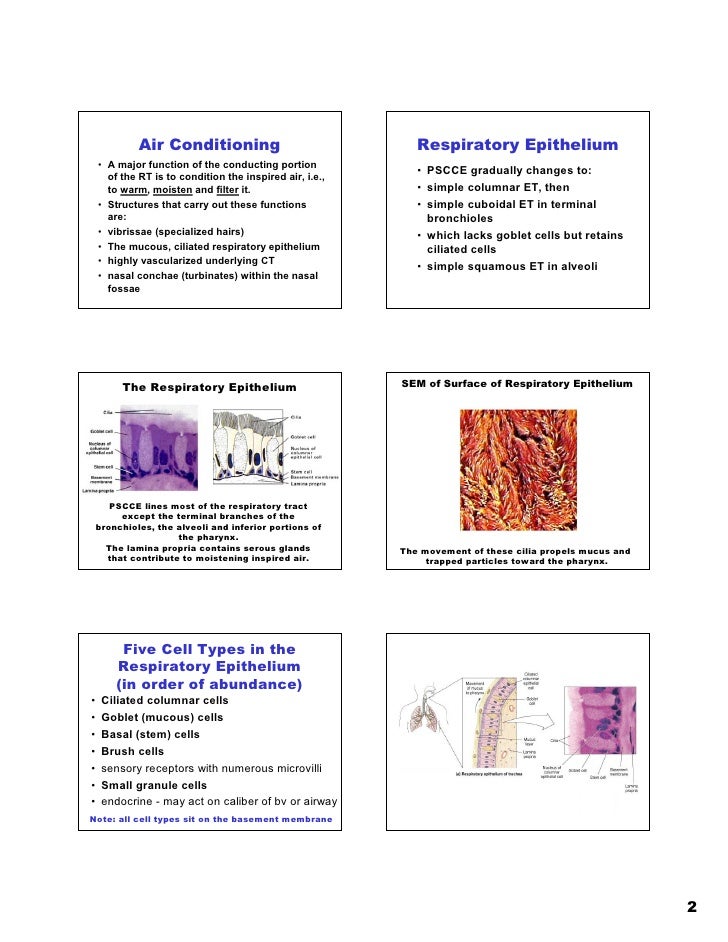
The respiratory system also helps us to smell and create sound. The following are the five key functions of the respiratory system. These cells are about 25 nm thick and are highly permeable to.
The respiratory system also respiratory apparatus ventilatory system is a biological system consisting of specific organs and structures used for gas exchange in animals and plantsThe anatomy and physiology that make this happen varies greatly depending on the size of the organism the environment in which it lives and its evolutionary history. The respiratory system is the organs and other parts of your body involved in breathing when you exchange oxygen and carbon dioxide. The neural networks direct muscles that form the walls of the thorax and abdomen and produce pressure gradients that move air into and out of the lungs.
Respiratory System - Science Quiz. Experimental evidence of PM25 damage on the respiratory system.
An instrument called a spirometer is used to measure the volume of air that moves into and out of the lungs and the process of taking the measurements is called spirometry.
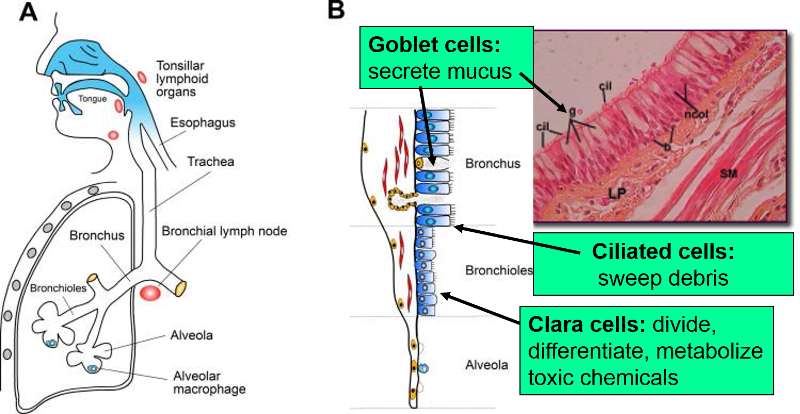
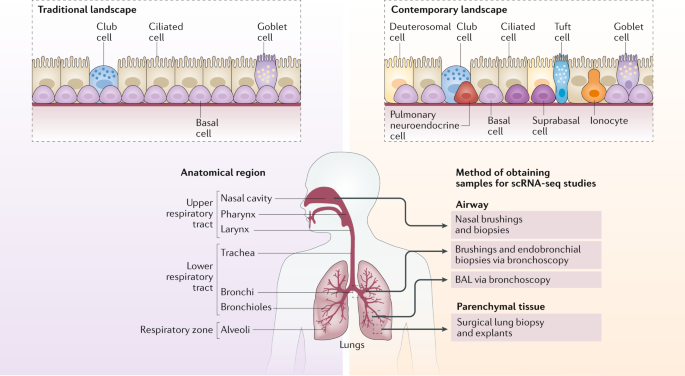
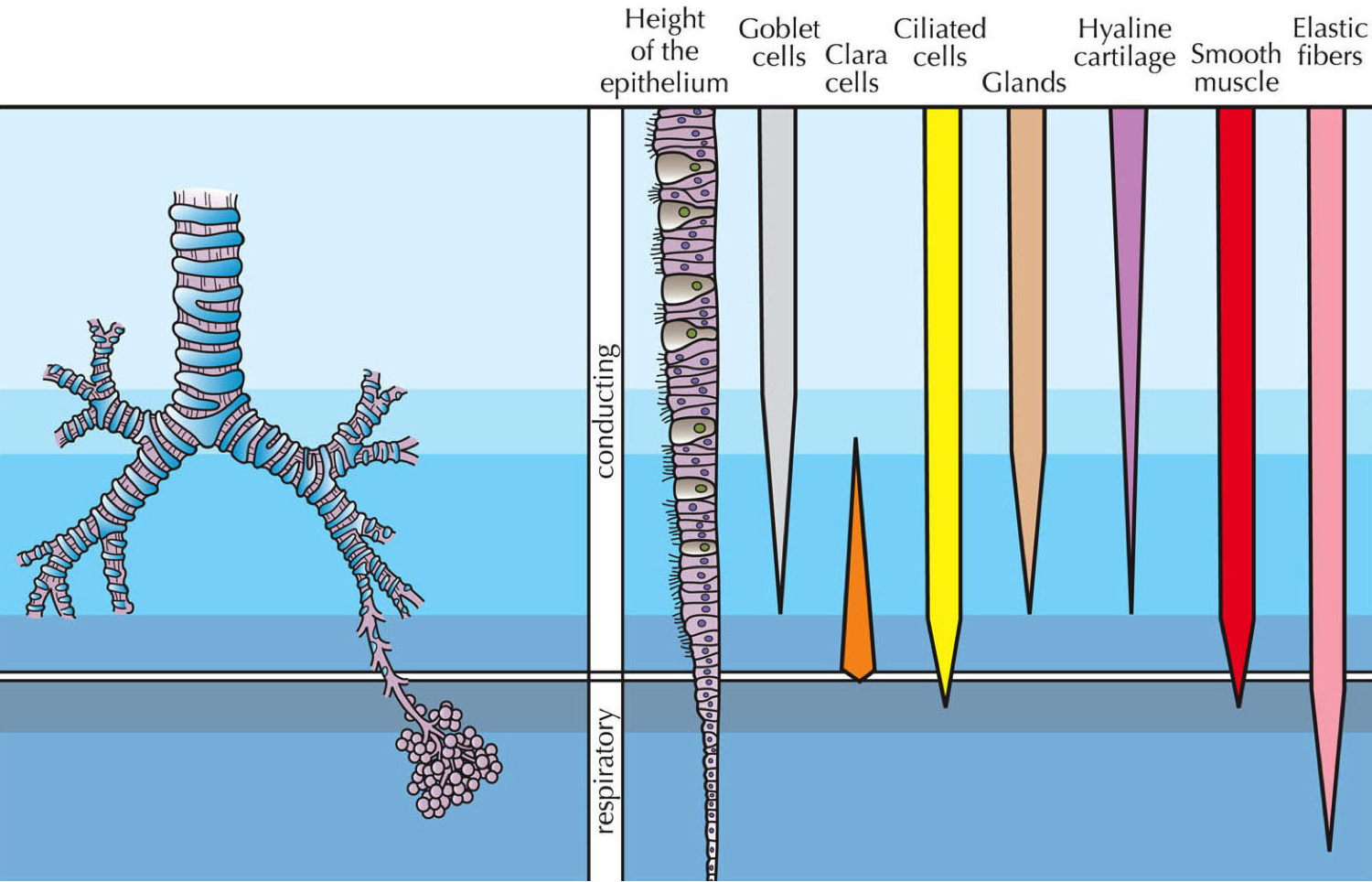
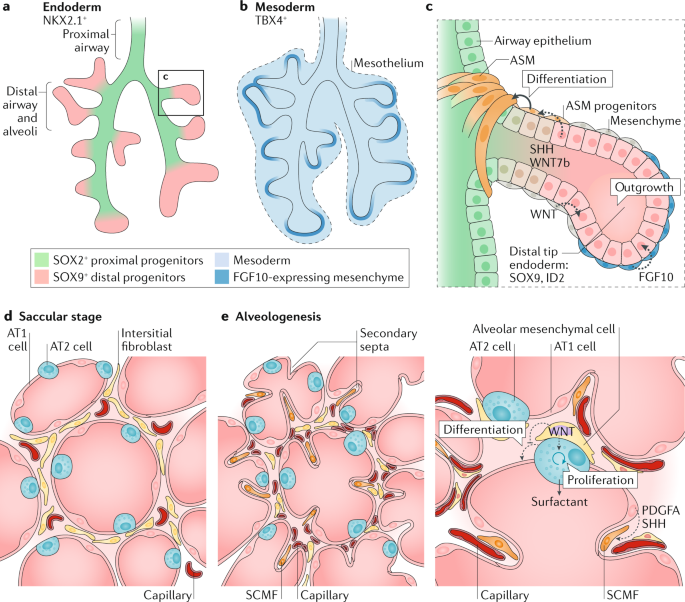
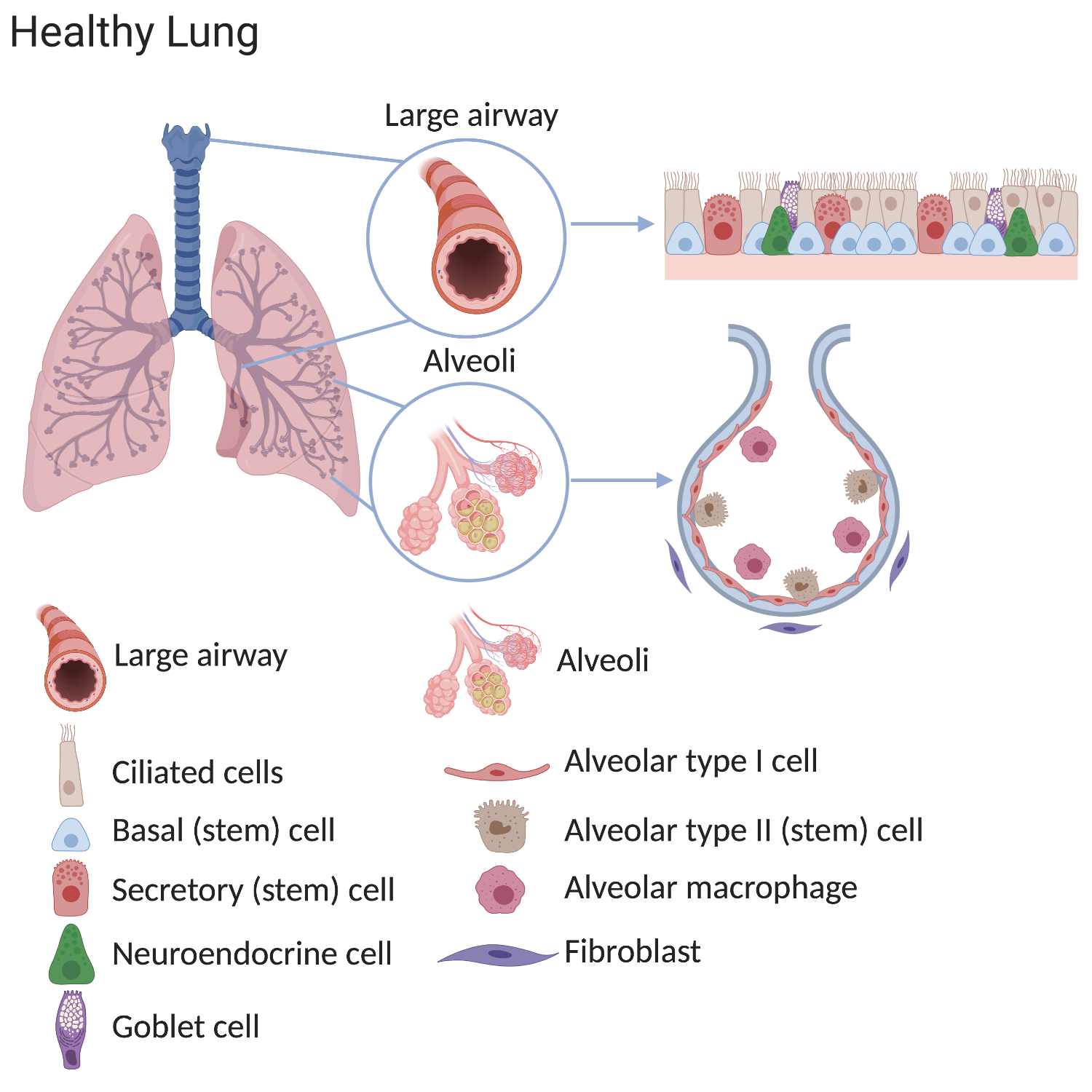
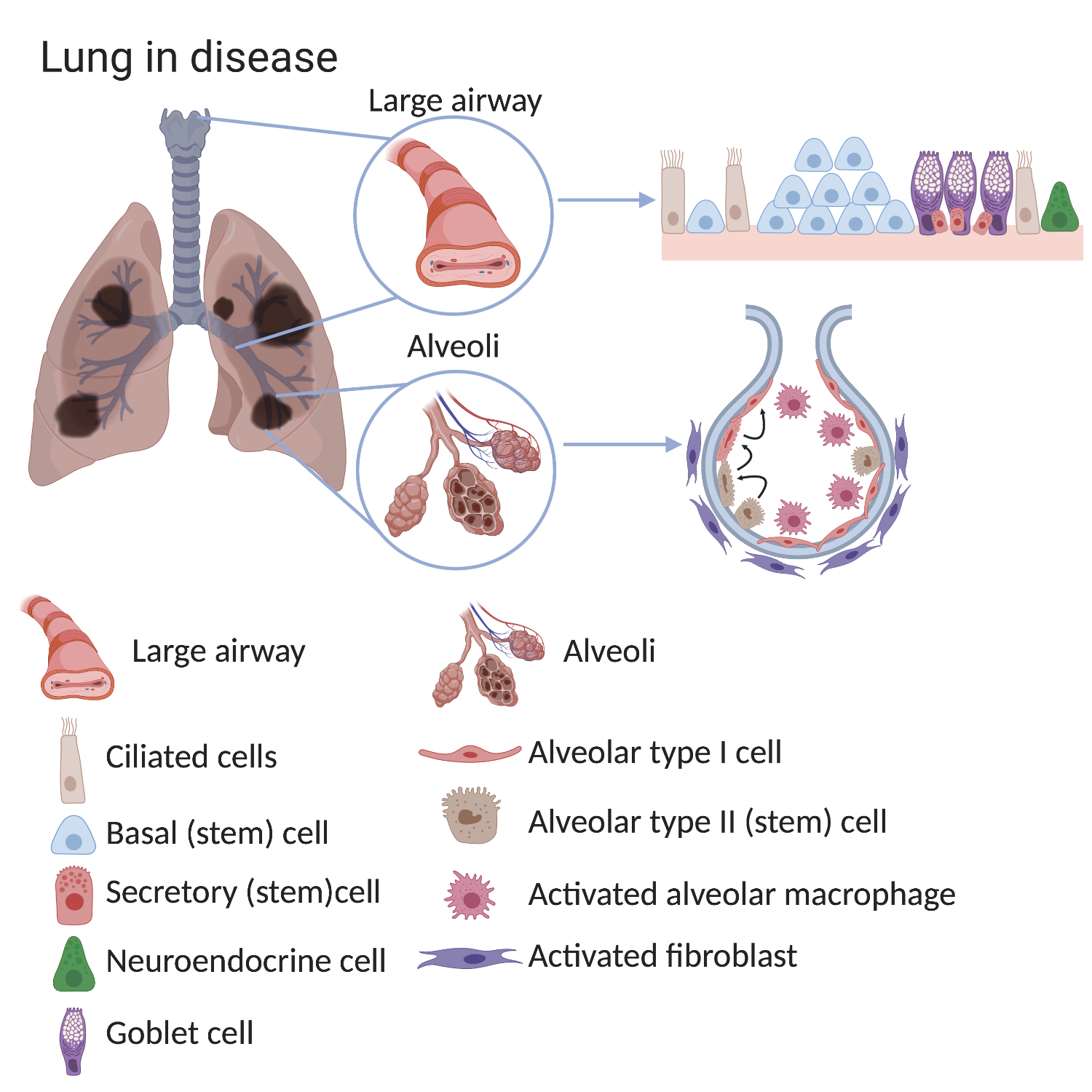
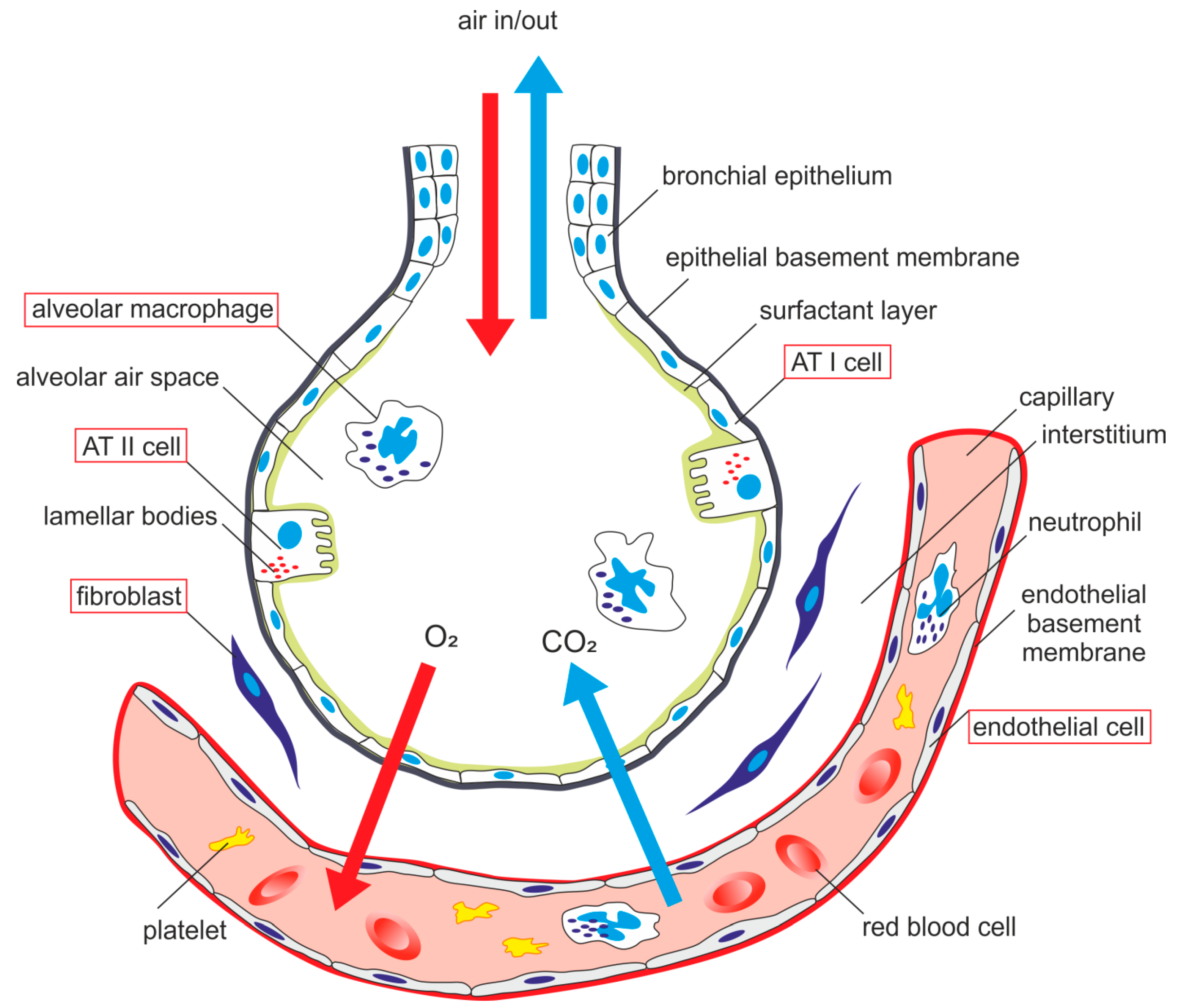
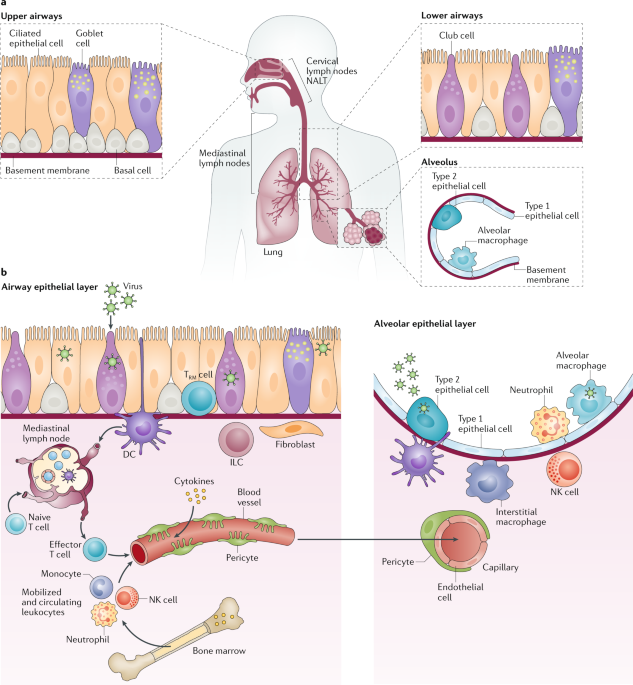
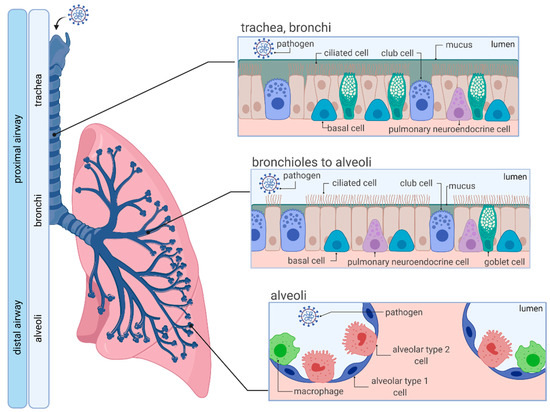
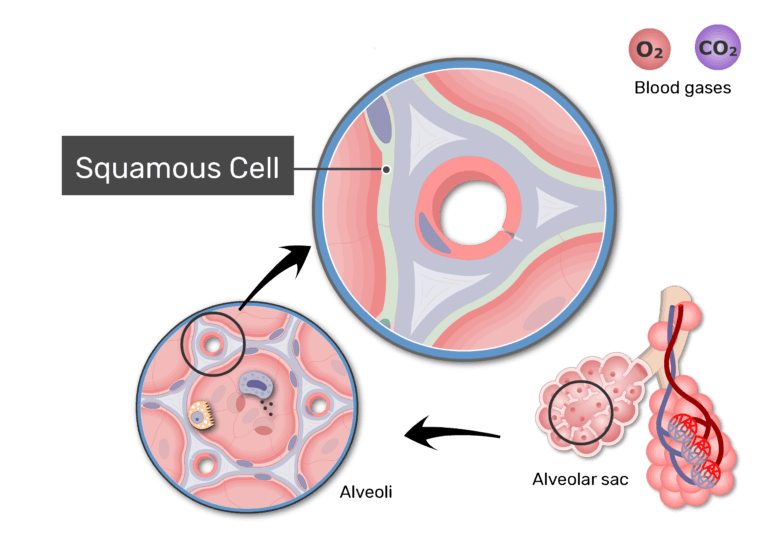
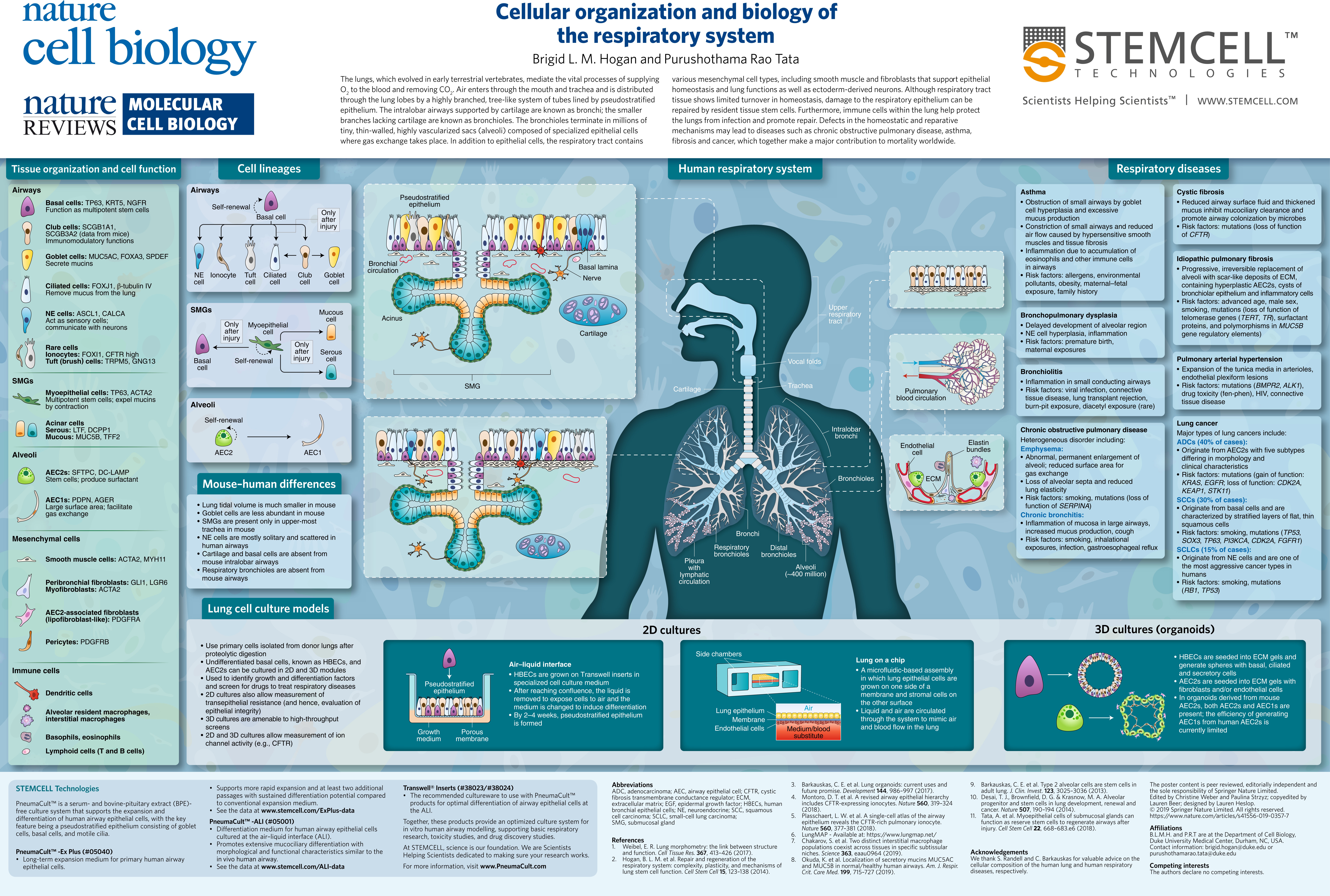
Type I alveolar cells type II alveolar cells and alveolar macrophages. The lower respiratory system includes the windpipe or trachea which separates into a pair of bronchial tubes that lead down into either lung. The primary function of this system is to provide body tissues and cells with life-giving oxygen while expelling carbon dioxide. Human and mouse Sox expression. The respiratory system is composed of a group of muscles blood vessels and organs that enable us to breathe. Human respiratory system the system in humans that takes up oxygen and expels carbon dioxide. The alveolar wall consists of three major cell types. The exchange of gases such as carbon dioxide and oxygen between the air and blood takes place in the lungsIn the alveoli balloon-like structures in the lungs gases diffuse between the inside and outside of the body by the process of simple diffusion based on concentration gradientA system of air passages brings the air to the respiratory membrane in the alveoli. Small cell lung cancer is most commonly found in.
Additionally the common laboratory mouse model C57BL6J completely lacks respiratory breathing movements seen in the human fetus. The structure and function of each cell type is briefly described below. Experimental evidence of PM25 damage on the respiratory system. Breathing is an automatic and rhythmic act produced by networks of neurons in the hindbrain the pons and medulla. Infections of the respiratory tract are grouped according to their symptomatology and anatomic involvement. A type I alveolar cell is a squamous epithelial cell of the alveoli which constitute up to 97 percent of the alveolar surface area. The body cells need a continuous supply of oxygen for the metabolic processes that are necessary to maintain life.











:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/respiration-58b9a1d93df78c353c0e3e0f.jpg)

/what-are-alveoli-2249043-01-94dfddd4dfe9488b8056d586824c7c36.png)
:background_color(FFFFFF):format(jpeg)/images/article/en/alveoli/oon7yrBXGYjGnowrXJQ_alveolus.png)










Post a Comment for "Respiratory System Cell Types"